Contents
[hide]- 1 Cannabis
- 2 Tryptamines
- 3 Phenethylamines
- 4 Beta-carbolines
- 4.1 Apocynaceae
- 4.2 Bignoniaceae
- 4.3 Calycanthaceae
- 4.4 Chenopodiaceae
- 4.5 Combretaceae
- 4.6 Cyperaceae
- 4.7 Elaeagnaceae
- 4.8 Gramineae
- 4.9 Lauraceae
- 4.10 Leguminosae
- 4.11 Loganiaceae
- 4.12 Malpighiaceae
- 4.13 Myristicaceae
- 4.14 Ochnaceae
- 4.15 Palmae
- 4.16 Papaveraceae
- 4.17 Passifloraceae
- 4.18 Polygonaceae
- 4.19 Rubiaceae
- 4.20 Rutaceae
- 4.21 Sapotaceae
- 4.22 Simaroubaceae
- 4.23 Solanaceae
- 4.24 Symplocaceae
- 4.25 Tiliaceae
- 4.26 Zygophyllaceae
- 5 Plants containing other psychoactive substances
- 6 See also
- 7 References
- 8 Bibliography
- 9 External links
Cannabis[edit]
Main article: Cannabis
Cannabis (Marijuana) is a popular psychoactive plant that is often used medically and recreationally. Cannabis is also unique in that it contains a psychoactive substance, THC, which contains no nitrogen and is not an indole, tryptamine, phenethylamine, anticholinergic (deliriant), or a dissociative drug. Cannabis plants tend to vary, with different strains producing dynamic balances of psychoactive cannabinoids (THC, CBD, etc.) that cause different strains to produce markedly different effects, popular strains often being hybrids of both Cannabis sativa and Cannabis indica. Some universities and research firms currently study the medicinal effects of cannabis. Many jurisdictions have laws regulating (or outright prohibiting) the sale and use of medical cannabis to treat pain, insomnia, and stimulate appetite.Tryptamines[edit]

DMT Molecule in 2D
Acanthaceae[edit]
Species, Alkaloid content, where given, refers to dried material- Fittonia albivenis, a common ornamental plant from South America. It is useful in the treatment of headaches, etc.
- Justicia pectoralis, DMT in leaves
Aceraceae[edit]
- Acer saccharinum (Silver Maple Tree) was found to contain the indole alkaloid gramine (not active and extremely toxic) 0.05% in the leaves, so it is possible that other members of this plant family contain active compounds.[1]
Aizoaceae[edit]
- Delosperma acuminatum, DMT, 5-MEO-DMT[2]
- Delosperma cooperi, DMT, 5-MEO-DMT[2]

- Delosperma ecklonis, DMT[2]
- Delosperma esterhuyseniae, DMT[2]
- Delosperma hallii, 5-MEO-DMT[2]
- Delosperma harazianum, DMT, 5-MEO-DMT[2]
- Delosperma harazianum
Shibam, DMT[2]
- Delosperma harazianum
- Delosperma hirtum, DMT[2]
- Delosperma hallii
aff. litorale
- Delosperma hallii
- Delosperma lydenbergense, DMT, 5-MEO-DMT[2]
- Delosperma nubigenum, 5-MEO-DMT[2]

- Delosperma pageanum, DMT, 5-MEO-DMT[2]
- Delosperma pergamentaceum, Traces of DMT[2]
- Delosperma tradescantioides, DMT[2]
Apocynaceae[edit]
Fabaceae (Leguminosae)[edit]
- Acacia acuminata, Up to 1.5% alkaloids, mainly consisting of dimethyltryptamine in bark & leaf[4] Also, Harman, Tryptamine, NMT, other alkaloids in leaf.[5]
 Acacia alpina, Active principles in leaf[6]
Acacia alpina, Active principles in leaf[6] Acacia angustissima, β-methyl-phenethylamine,[7] NMT and DMT in leaf (1.1-10.2 ppm)[8]
Acacia angustissima, β-methyl-phenethylamine,[7] NMT and DMT in leaf (1.1-10.2 ppm)[8] Acacia aroma, Tryptamine alkaloids.[9] Significant amount of tryptamine in the seeds.[10]
Acacia aroma, Tryptamine alkaloids.[9] Significant amount of tryptamine in the seeds.[10] Acacia auriculiformis, 5-MeO-DMT in stem bark[11]
Acacia auriculiformis, 5-MeO-DMT in stem bark[11] Acacia baileyana, 0.02% tryptamine and β-carbolines, in the leaf, Tetrahydroharman[12]
Acacia baileyana, 0.02% tryptamine and β-carbolines, in the leaf, Tetrahydroharman[12]- Acacia beauverdiana, Psychoactive[13] Ash used in Pituri.[14]
 Acacia berlandieri, DMT, amphetamines, mescaline, nicotine[15]
Acacia berlandieri, DMT, amphetamines, mescaline, nicotine[15] Acacia catechu, DMT[2] and other tryptamines in leaf, bark
Acacia catechu, DMT[2] and other tryptamines in leaf, bark Acacia caven, Psychoactive[16]
Acacia caven, Psychoactive[16]- Acacia chundra, DMT and other tryptamines in leaf, bark
- Acacia colei, DMT[17]
- Acacia complanata, 0.3% alkaloids in leaf and stem, almost all N-methyl-tetrahydroharman, with traces of tetrahydroharman, some of tryptamine[18][19][20]
 Acacia confusa, DMT & NMT in leaf, stem & bark 0.04% NMT and 0.02% DMT in stem.[6] Also N,N-dimethyltryptamine N-oxide[21]
Acacia confusa, DMT & NMT in leaf, stem & bark 0.04% NMT and 0.02% DMT in stem.[6] Also N,N-dimethyltryptamine N-oxide[21] Acacia cornigera, Psychoactive,[16] Tryptamines[22] DMT according to C. Rastch.
Acacia cornigera, Psychoactive,[16] Tryptamines[22] DMT according to C. Rastch. Acacia cultriformis, Tryptamine, in the leaf, stem[6] and seeds.[10] Phenethylamine in leaf and seeds[10]
Acacia cultriformis, Tryptamine, in the leaf, stem[6] and seeds.[10] Phenethylamine in leaf and seeds[10]- Acacia cuthbertsonii, Psychoactive[13]
 Acacia decurrens, Psychoactive,[16] but less than 0.02% alkaloids[12]
Acacia decurrens, Psychoactive,[16] but less than 0.02% alkaloids[12]- Acacia delibrata, Psychoactive[13]
- Acacia falcata, Psychoactive,[13] but less than 0.02% alkaloids[12] Psychoactive 0.2-0.3% alkaloids[23]
 Acacia farnesiana, Traces of 5-MeO-DMT[24] in fruit. β-methyl-phenethylamine, flower.[25] Ether extracts about 2-6% of the dried leaf mass.[26] Alkaloids are present in the bark[27] and leaves.[28] Amphetamines and mescaline also found in tree.[22]
Acacia farnesiana, Traces of 5-MeO-DMT[24] in fruit. β-methyl-phenethylamine, flower.[25] Ether extracts about 2-6% of the dried leaf mass.[26] Alkaloids are present in the bark[27] and leaves.[28] Amphetamines and mescaline also found in tree.[22]- Acacia flavescens, Strongly Psychoactive, Bark.
- Acacia floribunda, Tryptamine, phenethylamine,[29] in flowers[10] other tryptamines,[30] DMT,tryptamine,NMT 0.3-0.4% phyllodes.[31]
- Acacia georginae, Psychoactive,[16] plus deadly toxins
 Acacia horrida, Psychoactive[16]
Acacia horrida, Psychoactive[16] Acacia implexa, Psychoactive[32]
Acacia implexa, Psychoactive[32]- Acacia jurema, DMT, NMT
 Acacia karroo, Psychoactive
Acacia karroo, Psychoactive- Acacia laeta, DMT, in the leaf[6]
 Acacia longifolia, 0.2% tryptamine in bark, leaves, some in flowers, phenylethylamine in flowers,[29] 0.2% DMT in plant.[33] Histamine alkaloids.[12]
Acacia longifolia, 0.2% tryptamine in bark, leaves, some in flowers, phenylethylamine in flowers,[29] 0.2% DMT in plant.[33] Histamine alkaloids.[12]- Acacia sophorae, Tryptamine in leaves, bark[10]
- Acacia macradenia, Tryptamine[10]
 Acacia maidenii, 0.6% NMT and DMT in about a 2:3 ratio in the stem bark, both present in leaves[6]
Acacia maidenii, 0.6% NMT and DMT in about a 2:3 ratio in the stem bark, both present in leaves[6] Acacia mangium, Psychoactive[16]
Acacia mangium, Psychoactive[16] Acacia melanoxylon, DMT, in the bark and leaf,[34] but less than 0.02% total alkaloids[12]
Acacia melanoxylon, DMT, in the bark and leaf,[34] but less than 0.02% total alkaloids[12] Acacia mellifera, DMT, in the leaf[6]
Acacia mellifera, DMT, in the leaf[6] Acacia nilotica, DMT, in the leaf[6]
Acacia nilotica, DMT, in the leaf[6]- Acacia nilotica subsp. adstringens, Psychoactive, DMT in the leaf
- Acacia neurophylla DMT in bark, Harman in leaf.[35]
- Acacia obtusifolia, Tryptamine, DMT, NMT, other tryptamines,[32] 0.4-0.5% in dried bark,0.15-0.2% in leaf, 0.07% in branch tips.[36]
- Acacia oerfota, Less than 0.1% DMT in leaf,[37] NMT
- Acacia penninervis, Psychoactive[13]
 Acacia phlebophylla, 0.3% DMT in leaf, NMT[6]
Acacia phlebophylla, 0.3% DMT in leaf, NMT[6] Acacia podalyriaefolia, Tryptamine in the leaf,[6] 0.5% to 2% DMT in fresh bark, phenethylamine, trace amounts.[29] Although this species is claimed to contain 0.5% to 2% DMT in fresh bark the reference for this is invalid as there is no reference to Acacia Podalyriffolia anywhere in the reference article. Additionally, well known and proven extraction techniques for DMT have failed to produce any DMT or alkaloids from fresh bark or the leaves on multiple sample taken at various seasons. Should DMT actually exist in this species of Acacia then it exists in extremely small amounts and have failed to produce any alkaloids with Acid/Base extraction techniques using HCl/Na(OH)2. On the same note, more academic research is definitely required into the DMT content of this and other Australian Acacia species with proper chemical analysis of sample.[citation needed]
Acacia podalyriaefolia, Tryptamine in the leaf,[6] 0.5% to 2% DMT in fresh bark, phenethylamine, trace amounts.[29] Although this species is claimed to contain 0.5% to 2% DMT in fresh bark the reference for this is invalid as there is no reference to Acacia Podalyriffolia anywhere in the reference article. Additionally, well known and proven extraction techniques for DMT have failed to produce any DMT or alkaloids from fresh bark or the leaves on multiple sample taken at various seasons. Should DMT actually exist in this species of Acacia then it exists in extremely small amounts and have failed to produce any alkaloids with Acid/Base extraction techniques using HCl/Na(OH)2. On the same note, more academic research is definitely required into the DMT content of this and other Australian Acacia species with proper chemical analysis of sample.[citation needed] Acacia polyacantha, DMT in leaf[6] and other tryptamines in leaf, bark
Acacia polyacantha, DMT in leaf[6] and other tryptamines in leaf, bark- Acacia polyacantha ssp. campylacantha, Less than 0.2% DMT in leaf, NMT; DMT and other tryptamines in leaf, bark[38]
 Acacia rigidula, DMT, NMT, tryptamine, traces of amphetamines, mescaline, nicotine and others[39]
Acacia rigidula, DMT, NMT, tryptamine, traces of amphetamines, mescaline, nicotine and others[39]- Acacia sassa, Psychoactive[16]
 Acacia schaffneri, β-methyl-phenethylamine, Phenethylamine[40] Amphetamines and mescaline also found.[22]
Acacia schaffneri, β-methyl-phenethylamine, Phenethylamine[40] Amphetamines and mescaline also found.[22] Acacia senegal, Less than 0.1% DMT in leaf,[6] NMT, other tryptamines. DMT in plant,[25] DMT in bark.[10]
Acacia senegal, Less than 0.1% DMT in leaf,[6] NMT, other tryptamines. DMT in plant,[25] DMT in bark.[10]- Acacia seyal, DMT, in the leaf.[6] Ether extracts about 1-7% of the dried leaf mass.[26]
 Acacia sieberiana, DMT, in the leaf[6]
Acacia sieberiana, DMT, in the leaf[6] Acacia simplex, DMT and NMT, in the leaf, stem and trunk bark, 0.81% DMT in bark, MMT[6][41]
Acacia simplex, DMT and NMT, in the leaf, stem and trunk bark, 0.81% DMT in bark, MMT[6][41] Acacia tortilis, DMT, NMT, and other tryptamines[32]
Acacia tortilis, DMT, NMT, and other tryptamines[32] Acacia vestita, Tryptamine, in the leaf and stem,[6] but less than 0.02% total alkaloids[12]
Acacia vestita, Tryptamine, in the leaf and stem,[6] but less than 0.02% total alkaloids[12]- Acacia victoriae, Tryptamines, 5-MeO-alkyltryptamine[10]
- List of Acacia Species Having Little or No Alkaloids in the Material Sampled:[12]
(0% C
C  0.02%, Concentration of Alkaloids)
0.02%, Concentration of Alkaloids)
- Albizia inundata leaves contain DMT.[16]
 Anadenanthera colubrina, Bufotenin, Beans,[42][43] Bufotenin oxide, Beans,[42] N,N-Dimethyltryptamine, Beans,[42][43] pods,[42]
Anadenanthera colubrina, Bufotenin, Beans,[42][43] Bufotenin oxide, Beans,[42] N,N-Dimethyltryptamine, Beans,[42][43] pods,[42]- Anadenanthera colubrina var. cebil - Bufotenin and Dimethyltryptamine have been isolated from the seeds and seed pods, 5-MeO-DMT from the bark of the stems.[44] The seeds were found to contain 12.4% bufotenine, 0.06% 5-MeO-DMT and 0.06% DMT.[45]
 Anadenanthera peregrina,
Anadenanthera peregrina,
- Anadenanthera peregrina var. peregrina, Bufotenine is in the seeds.[47]
 Desmanthus illinoensis, 0% - 0.34% DMT in root bark, highly variable.[48] Also NMT, N-hydroxy-N-methyltryptamine, 2-hydroxy-N-methyltryptamine, and gramine (toxic).[49]
Desmanthus illinoensis, 0% - 0.34% DMT in root bark, highly variable.[48] Also NMT, N-hydroxy-N-methyltryptamine, 2-hydroxy-N-methyltryptamine, and gramine (toxic).[49] Desmanthus leptolobus, 0.14% DMT in root bark, more reliable than D. illinoensis[48]
Desmanthus leptolobus, 0.14% DMT in root bark, more reliable than D. illinoensis[48]- Desmodium caudatum[50] (syn. Ohwia caudata ), Roots: 0.087% DMT,
- Desmodium intortum, Bufotentine, DMT[51]
 Codariocalyx motorius(syn. Desmodium gyrans), DMT, 5-MEO-DMT, leaves, roots
Codariocalyx motorius(syn. Desmodium gyrans), DMT, 5-MEO-DMT, leaves, roots- Desmodium racemosum, 5-MEO-DMT
 Desmodium triflorum, 0.0004% DMT-N-oxide, roots,[52] less in stems[52] and trace in leaves.[52]
Desmodium triflorum, 0.0004% DMT-N-oxide, roots,[52] less in stems[52] and trace in leaves.[52]- Leonurus sibiricus, Alkaloids
 Lespedeza capitata,
Lespedeza capitata, Lespedeza bicolor, DMT, 5-MEO-DMT in leaves and roots[53]
Lespedeza bicolor, DMT, 5-MEO-DMT in leaves and roots[53]- Lespedeza bicolor var. japonica, DMT, 5-MEO-DMT in leaves and root bark
- Mimosa ophthalmocentra, Dried root: DMT 1.6%, NMT 0.0012% and hordenine 0.0065%[54]
 Mimosa scabrella, Tryptamine, NMT, DMT and N-methyltetrahydrocarboline in bark[55]
Mimosa scabrella, Tryptamine, NMT, DMT and N-methyltetrahydrocarboline in bark[55]- Mimosa somnians, Trytamines and MMT
 Mimosa tenuiflora (syn. "Mimosa hostilis"), 0.31-0.57% DMT (dry root bark).[56] mimosa hostilis contains dmt and 5-meo-dmt.
Mimosa tenuiflora (syn. "Mimosa hostilis"), 0.31-0.57% DMT (dry root bark).[56] mimosa hostilis contains dmt and 5-meo-dmt. Mimosa verrucosa, DMT[57] in root bark
Mimosa verrucosa, DMT[57] in root bark Mucuna pruriens, "The leaves, seeds, stems and roots contain L-Dopa, Serotonin, 5-HTP, and Nicotine, as well as N,N-DMT, Bufotenine, and 5-MeO-DMT."[58]
Mucuna pruriens, "The leaves, seeds, stems and roots contain L-Dopa, Serotonin, 5-HTP, and Nicotine, as well as N,N-DMT, Bufotenine, and 5-MeO-DMT."[58]- Petalostylis casseoides, 0.4-0.5% tryptamine, DMT, etc. in leaves and stems[53]
- Petalostylis labicheoides var. casseoides, DMT in leaves and stems
- Phyllodium pulchellum(syn. Desmodium pulchellum), 0.2% 5-MeO-DMT, small quantities of DMT[53] DMT (dominates in seedlings and young plants), 5-MEO-DMT (dominates in mature plant), whole plant, roots, stems, leaves, flowers
- Erythrina flabelliformis, other Erythrina species, seeds contain the alkaloids Erysodin and Erysovin[59]
Caesalpinioideae subfamily[edit]
- Petalostylis cassioides: 0.4-0.5% tryptamine, DMT, etc. in leaves and stems[60]
- Petalostylis labicheoides, Tryptamines in leaves and stems, MAO's up to 0.5%[61]
- Lauraceae
Malpighiaceae[edit]
- Diplopterys cabrerana: DMT 0.17-1.74%, average of 0.47% DMT[62]
Myristicaceae[edit]
- Horsfieldia superba: 5-MeO-DMT[53] and beta-carbolines[60]
- Iryanthera macrophylla: 5-MeO-DMT in bark[53]
- Iryanthera ulei: 5-MeO-DMT in bark
- Osteophloem platyspermum: DMT, 5-MeO-DMT in bark
- Virola calophylla, Leaves 0.149% DMT, leaves 0.006% MMT 5-MeO-DMT in bark[63]
- Virola callophylloidea, DMT
- Virola carinata, DMT in leaves
- Virola cuspidata, DMT[61]
- Virola divergens, DMT in leaves
 Virola elongata(syn. Virola theiodora), DMT, 5-MEO-DMT in bark, roots, leaves and flowers
Virola elongata(syn. Virola theiodora), DMT, 5-MEO-DMT in bark, roots, leaves and flowers- Virola melinonii, DMT in bark
- Virola multinervia, DMT, 5-MEO-DMT in bark and roots
- Virola pavonis, DMT in leaves
- Virola peruviana, 5-MEO-DMT, traces of DMT and 5-MeO-tryptamine in bark
- Virola rufula, Alkaloids in bark and root, 95% of which is MeO-DMT[64] 0.190% 5-MeO-DMT in bark, 0.135% 5-MeO-DMT in root, 0.092% DMT in leaves.
- Virola sebifera, The bark contains 0.065% to 0.25% alkaloids, most of which are DMT and 5-MeO-DMT.[65]
- Virola surinamensis, DMT[61] in bark
- Virola venosa, DMT, 5-MEO-DMT in roots, leaves DMT
Ochnaceae[edit]
- Testulea gabonensis: 0.2% 5-MeO-DMT, small quantities of DMT,[53] DMT in bark and root bark, NMT
Ochnaceae[edit]
Poaceae (Gramineae)[edit]
Some Graminae (grass) species contain gramine, which can cause brain damage, other organ damage, central nervous system damage and death in sheep.[66] Arundo donax, 0.0057% DMT in dried rhizome, no stem, 0.026% bufotenine, 0.0023% 5-MeO-MMT[67]
Arundo donax, 0.0057% DMT in dried rhizome, no stem, 0.026% bufotenine, 0.0023% 5-MeO-MMT[67] Phalaris aquatica, 0.0007-0.18% Total alkaloids,[68] 0.100% DMT,[69] 0.022% 5-MeO-DMT,[69] 0.005% 5-OH-DMT[69]
Phalaris aquatica, 0.0007-0.18% Total alkaloids,[68] 0.100% DMT,[69] 0.022% 5-MeO-DMT,[69] 0.005% 5-OH-DMT[69] Phalaris arundinacea, 0.0004-0.121% Total alkaloids[68]
Phalaris arundinacea, 0.0004-0.121% Total alkaloids[68]- Phalaris brachystachys, Aerial parts up to 3% total alkaloids, DMT present[citation needed]
 Phragmites australis, DMT in roots. None of the above alkaloids are said to have been found in Phalaris californica, Phalaris canariensis, Phalaris minor and hybrids of P. arundinacea together with P. aquatica.[68]
Phragmites australis, DMT in roots. None of the above alkaloids are said to have been found in Phalaris californica, Phalaris canariensis, Phalaris minor and hybrids of P. arundinacea together with P. aquatica.[68]
Polygonaceae[edit]
- Erigonum sp.: DMT
Punicaceae[edit]
- Punica granatum "DMT in root cortex;"[61] The dried stem and root bark of the tree contain about 0.4-0.9% alkaloids.[70]
Rubiaceae[edit]
- Mitragyna speciosa, 7-hydroxymitragynine [71]
- Psychotria carthagenensis, 0.2% average DMT in dried leaves
- Psychotria expansa, DMT[61]
- Psychotria forsteriana, DMT[61]
- Psychotria insularum, DMT[61]
 Psychotria poeppigiana,[72] DMT[61]
Psychotria poeppigiana,[72] DMT[61]- Psychotria rostrata, DMT[61]
- Psychotria rufipilis, DMT[61]
 Psychotria viridis, DMT 0.1-0.61% dried mass.[73]
Psychotria viridis, DMT 0.1-0.61% dried mass.[73]
Rutaceae[74][75][edit]
 Dictyoloma incanescens, 5-MeO-DMT in leaves,[64] 0.04% 5-MeO-DMT in bark[53]
Dictyoloma incanescens, 5-MeO-DMT in leaves,[64] 0.04% 5-MeO-DMT in bark[53]- Dutaillyea drupacea, > 0.4% 5-MeO-DMT in leaves[32]
- Dutaillyea oreophila, 5-MeO-DMT in leaves
 Tetradium ruticarpum(syn. Evodia rutaecarpa), 5-MeO-DMT in leaves, fruit and roots
Tetradium ruticarpum(syn. Evodia rutaecarpa), 5-MeO-DMT in leaves, fruit and roots Limonia acidissima, 5-MeO-DMT in stems
Limonia acidissima, 5-MeO-DMT in stems- Euodia leptococca (formerly Melicope), 0.2% total alkaloids, 0.07% 5-MeO-DMT; 5-MeO-DMT in leaves and stems, also "5-MeO-DMT-Oxide and a beta-carboline"[60]
- Pilocarpus organensis, 5-MeO-DMT in leaves
- Vepris ampody, Up to 0.2% DMT in leaves and branches[53]
- Zanthoxylum arborescens, DMT in leaves
- Zanthoxylum procerum, DMT in leaves
Urticaceae[edit]
- Urtica pilulifera: Bufotenin[61]
Phenethylamines[edit]
Species, Alkaloid Content (Fresh) - Alkaloid Content (Dried)- Echinopsis lageniformis
 (syn. Trichocereus bridgesii), Mescaline > 0.025%,[76] also 3,4-dimethoxyphenylethylamine < 1%, 3-methoxytyramine < 1%, tyramine < 1% - Mescaline 2%[77]
(syn. Trichocereus bridgesii), Mescaline > 0.025%,[76] also 3,4-dimethoxyphenylethylamine < 1%, 3-methoxytyramine < 1%, tyramine < 1% - Mescaline 2%[77] - Echinopsis scopulicola
 (syn. Trichocereus scopulicola), Mescaline[78]
(syn. Trichocereus scopulicola), Mescaline[78] - Echinopsis pachanoi
 (syn. Trichocereus pachanoi), Mescaline 0.006-0.12%, 0.05% Average[79] - Mescaline 0.01%-2.375%[79]
(syn. Trichocereus pachanoi), Mescaline 0.006-0.12%, 0.05% Average[79] - Mescaline 0.01%-2.375%[79] - Echinopsis spachiana
 (syn. Trichocereus spachianus), Mescaline[80] - Mescaline[80]
(syn. Trichocereus spachianus), Mescaline[80] - Mescaline[80] - Lophophora williamsii
 (Peyote), 0.4% Mescaline[78] - 3-6% Mescaline[80]
(Peyote), 0.4% Mescaline[78] - 3-6% Mescaline[80] - Opuntia acanthocarpa
 Mescaline[80]
Mescaline[80] - Opuntia basilaris
 Mescaline 0.01%, plus 4-hydroxy-3-5-dimethoxyphenethylamine[80]
Mescaline 0.01%, plus 4-hydroxy-3-5-dimethoxyphenethylamine[80] - Austrocylindropuntia cylindrica (syn. Opuntia cylindrica),[81] Mescaline[80]
- Cylindropuntia echinocarpa
 (syn. Opuntia echinocarpa), Mescaline 0.01%, 3-4-dimethoxyphenethylamine 0.01%, 4-hydroxy-3-5-dimethoxyphenethylamine 0.01%[80]
(syn. Opuntia echinocarpa), Mescaline 0.01%, 3-4-dimethoxyphenethylamine 0.01%, 4-hydroxy-3-5-dimethoxyphenethylamine 0.01%[80] - Cylindropuntia spinosior (syn. Opuntia spinosior),[82] Mescaline 0.00004%, 3-methoxytyramine 0.001%, tyramine 0.002%, 3-4-dimethoxyphenethylamine.[80]
- Echinopsis macrogona
 (syn. Trichocereus macrogonus), > 0.01-0.05% Mescaline[83]
(syn. Trichocereus macrogonus), > 0.01-0.05% Mescaline[83] - Echinopsis peruviana
 (syn. Trichocereus peruvianus), Mescaline 0.0005%-0.12%[79] - Mescaline
(syn. Trichocereus peruvianus), Mescaline 0.0005%-0.12%[79] - Mescaline - Echinopsis tacaquirensis subsp. taquimbalensis (syn. Trichocereus taquimbalensis),[84] > 0.005-0.025% Mescaline[83]
- Echinopsis terscheckii
 (syn. Trichocereus terscheckii, Trichocereus werdemannianus)[85] > 0.005-0.025% Mescaline[83] - Mescaline 0.01%-2.375%[79]
(syn. Trichocereus terscheckii, Trichocereus werdemannianus)[85] > 0.005-0.025% Mescaline[83] - Mescaline 0.01%-2.375%[79] - Echinopsis valida, 0.025% Mescaline[78]
- Pelecyphora aselliformis, Mescaline[78]
Beta-carbolines[edit]
Harmaline, a Beta-carboline
Apocynaceae[edit]
- Amsonia tabernaemontana, Harmine
- Aspidosperma exalatum, Beta-carbolines[86]
- Aspidosperma polyneuron, Beta-carbolines[86]
- Apocynum cannabinum, Harmalol
- Ochrosia nakaiana, Harman
- Pleicarpa mutica, Beta-carbolines[86]
Bignoniaceae[edit]
- Newbouldia laevis, Harman
Calycanthaceae[edit]
Chenopodiaceae[edit]
- Hammada leptoclada, Tetrahydroharman, etc.
- Kochia scoparia, Harmine, etc.
Combretaceae[edit]
- Guiera senegalensis, Harman, etc.
Cyperaceae[edit]
- Carex brevicollis, Harmine, etc.
- Carex parva, Beta-carbolines[86]
Elaeagnaceae[edit]
- Elaeagnus angustifolia, Harman, etc.

- Elaeagnus commutata, Beta-carbolines[86]
- Elaeagnus hortensis, Tetrahydroharman, etc.
- Elaeagnus orientalis, Tetrahydroharman
- Elaeagnus spinosa, Tetrahydroharman
- Hippophae rhamnoides, Harman, etc.
- Shepherdia argentea, Tetrahydroharmol

- Shepherdia canadensis, Tetrahydroharmol
Gramineae[edit]
- Arundo donax, Tetrahydroharman

- Festuca arundinacea, Harman, etc.

- Lolium perenne, (Perennial Ryegrass), Harman, etc.

- Phalaris aquatica, Beta-carbolines[86]
- Phalaris arundinacea, Beta-carbolines[86]
Lauraceae[edit]
- Nectandra megapotamica, Beta-carbolines[86]
Leguminosae[edit]
- Acacia baileyana, Tetrahydroharman
- Acacia complanata, Tetrahydroharman, etc.
- Burkea africana, Harman, etc.
- Desmodium gangeticum, Beta-carbolines[86]
- Desmodium gyrans, Beta-carbolines[86]
- Desmodium pulchellum, Harman, etc.
- Mucuna pruriens, 6-Methoxy-Harman
- Petalostylis labicheoides, Tetrahydroharman; MAO's up to 0.5%[61]
- Prosopis nigra, Harman, etc.
- Shepherdia pulchellum, Beta-carbolines[86]
Loganiaceae[edit]
- Strychnos melinoniana, Beta-carbolines[86]
- Strychnos usambarensis, Harman[86]
Malpighiaceae[edit]
- Banisteriopsis argentia, 5-methoxytetrahydroharman, (−)-N(6)-methoxytetrahydroharman, dimethyltryptamine-N(6)-oxide[7]
- Banisteriopsis caapi, Harmine 0.31-0.84%,[87] tetrahydroharmine, telepathine, dihydroshihunine,[88] 5-MeO-DMT in bark[89]

- Banisteriopsis inebrians, Beta-carbolines[86]
- Banisteriopsis lutea, Harmine, telepathine[7]
- Banisteriopsis metallicolor, Harmine, telepathine[7]
- Banisteriopsis muricata, Harmine up to 6%, harmaline up to 4%, plus DMT[90]
- Diplopterys cabrerana, Beta-carbolines[86]
- Cabi pratensis, Beta-carbolines[86]
- Callaeum antifebrile(syn. Cabi paraensis), Harmine
- Tetrapterys methystica(syn. Tetrapteris methystica), Harmine[91]
Myristicaceae[edit]
- Gymnacranthera paniculata, Beta-carbolines[86]
- Horsfieldia superba Beta-carbolines[60]
- Virola cuspidata, 6-Methoxy-Harman
- Virola rufula, Beta-carbolines[86]
- Virola theiodora, Beta-carbolines[86]
Ochnaceae[edit]
- Testulea gabonensis, Beta-carbolines[86]
Palmae[edit]
- Plectocomiopsis geminiflora, Beta-carbolines[86]
Papaveraceae[edit]
- Meconopsis horridula, Beta-carbolines[86]
- Meconopsis napaulensis, Beta-carbolines[86]

- Meconopsis paniculata, Beta-carbolines[86]
- Meconopsis robusta, Beta-carbolines[86]
- Meconopsis rudis, Beta-carbolines[86]
- Papaver rhoeas, Beta-carbolines[86]

Passifloraceae[edit]
- Passiflora actinia, Harman
- Passiflora alata, Harman
- Passiflora alba, Harman
- Passiflora bryonoides, Harman
- Passiflora caerulea, Harman

- Passiflora capsularis, Harman
- Passiflora decaisneana, Harman
- Passiflora edulis, Harman, 0-7001 ppm[25] in fruit

- Passiflora eichleriana, Harman
- Passiflora foetida, Harman

- Passiflora incarnata (with bee), Harmine, Harmaline, Harman, etc. 0.03%.[92] Alkaloids in rind of fruit 0.25%[92]

- Passiflora quadrangularis, Harman

- Passiflora ruberosa, Harman
- Passiflora subpeltata, Harman

- Passiflora warmingii, Harman
Polygonaceae[edit]
- Calligonum minimum, Beta-carbolines[86]
- Leptactinia densiflora, Leptaflorine, etc.
- Ophiorrhiza japonica, Harman
- Pauridiantha callicarpoides, Harman
- Pauridiantha dewevrei, Harman
- Pauridiantha lyalli, Harman
- Pauridiantha viridiflora, Harman
- Simira klugei, Harman
- Simira rubra, Harman
Rubiaceae[edit]
- Borreria verticillata, Beta-carbolines[86]
- Leptactinia densiflora, Beta-carbolines[86]
- Nauclea diderrichii, Beta-carbolines[86]
- Ophiorrhiza japonica, Beta-carbolines[86]
- Pauridiantha callicarpoides, Beta-carbolines[86]
- Pauridiantha dewevrei, Beta-carbolines[86]
- Pauridiantha yalli, Beta-carbolines[86]
- Pauridiantha viridiflora, Beta-carbolines[86]
- Pavetta lanceolata, Beta-carbolines[86]
- Psychotria carthagenensis, Beta-carbolines[86]
- Psychotria viridis, Beta-carbolines[86]
- Simira klugei, Beta-carbolines[86]
- Simira rubra, Beta-carbolines[86]
- Uncaria attenuata, Beta-carbolines[86]
- Uncaria canescens, Beta-carbolines[86]
- Uncaria orientalis, Beta-carbolines[86]
Rutaceae[edit]
- Tetradium (syn. Evodia) species: Some contain carbolines
- Euodia leptococca Beta-carboline[60]
- Araliopsis tabouensis, Beta-carbolines[86]
- Flindersia laevicarpa, Beta-carbolines[86]
- Xanthoxylum rhetsa, Beta-carbolines[86]
Sapotaceae[edit]
- Chrysophyllum lacourtianum, Norharman etc.
Simaroubaceae[edit]
- Ailanthus malabarica, Beta-carbolines.[86] See also Nag Champa.
- Perriera madagascariensis, Beta-carbolines[86]
- Picrasma ailanthoides, Beta-carbolines[86]
- Picrasma crenata, Beta-carbolines[86]
- Picrasma excelsa, Beta-carbolines[86]
- Picrasma javanica, Beta-carbolines[86]
Solanaceae[edit]
- Vestia foetida, (Syn V. lycioides) Beta-carbolines[86]

Symplocaceae[edit]
- Symplocos racemosa, Harman
Tiliaceae[edit]
- Grewia mollis, Beta-carbolines[86]
Zygophyllaceae[edit]
- Fagonia cretica, Harman

- Nitraria schoberi, Beta-carbolines[86]
- Peganum harmala, (Syrian Rue), The seeds contain about 2-6% alkaloids, most of which is harmaline.[93] Peganum harmala is also an abortifacient.

- Peganum nigellastrum, Harmine[94]
- Tribulus terrestris, Harman

- Zygophyllum fabago, Harman, harmine
Plants containing other psychoactive substances[edit]
Acoraceae: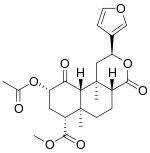 |  Salvia divinorum Salvia divinorum | Salvinorin A, 0.89-3.87 mg/g, also Salvinorin B and Salvinorin C[95] |
 |  Catha edulis Catha edulis | Khat[96] |
 |  Foeniculum vulgare Foeniculum vulgare | Unknown |
 | Unknown | |
 |  Laurelia novae-zelandiae Laurelia novae-zelandiae | Pukateine |
 |  Artemisia vulgaris Artemisia vulgaris | Thujone |
 |  Turnera diffusa Turnera diffusa | Damianin |
 |  Magnolia virginiana Magnolia virginiana | The leaves or bark have been placed in cupped hands over the nose and inhaled as a mild hallucinogen |
 |  Corydalis solida, Corydalis cava Corydalis solida, Corydalis cava | Bulbocapnine, Nantenine, Tetrahydropalmatine |
 |  Piper methysticum Piper methysticum | Kavalactones |
 |  Lagochilus inebrians Lagochilus inebrians | Lagochilin is thought to be responsible for the sedative, hypotensive and hemostatic effects of this plant. |
 |  Tagetes lucida Tagetes lucida | Anethole, Chavicol, Coumarin, Estragole, Isorhamnetin, Methyleugenol, Quercitin |
 |  Lactuca virosa Lactuca virosa | Lactucarium |
 |  Glaucium flavum Glaucium flavum | Glaucine |
 |  Galbulimima belgraveana Galbulimima belgraveana | Galbulimima belgraveana is rich in alkaloids and twenty-eight alkaloids have been isolated. Himbacine, himbeline, himandravine, himgravine, himbosine, himandridine, himandrine, G.B. 1, G. B. 2, G. B. 3, G. B. 4, G. B. 5, G. B. 6, G. B. 7, G. B. 8, G. B. 9, G. B. 10, G. B. 11, G. B. 12, himgaline, himbadine, G. B. 13, himgrine, G. B. 14, G. B. 15, G. B. 16, G. B. 17 and G. B. 18. |
 |  Zornia latifolia Zornia latifolia | Zornia latifolia, is mentioned in Food of the Gods as "an hallucinogenic substitute for cannabis". It's nicknamed Maconha brava because locals use it as a cannabis substitute. |
 |  Argemone mexicana Argemone mexicana | Used by Chinese residents of Mexico during the early 20th century as a legal substitute for opium and currently smoked as a marijuana substitute. |
 |  Argyreia nervosa (Hawaiian Baby Woodrose) Argyreia nervosa (Hawaiian Baby Woodrose) | Seeds contain high amounts of LSA (also known as d-lysergic acid amide, d-lysergamide, ergine, and LA-111), often 50-150X the amounts found in Ipomoea violacea. |
 |  Tabernanthe iboga Tabernanthe iboga | Ibogaine in root bark[97] |
 | Tabernanthe orientalis | Ibogaine in root leaves[97] |
 | Tabernanthe pubescens | Ibogaine and similar alkaloids[97] |
 | Tabernaemontana sp. | Ibogaine[97] |
 |  Trachelospermum jasminoides Trachelospermum jasminoides | Ibogaine[98] |
 |  Nymphaea caerulea Nymphaea caerulea | Recent studies have shown Nymphaea caerulea to have psychedelic properties, and may have been used as a sacrament in ancient Egypt and certain ancient South American cultures. Dosages of 5 to 10 grams of the flowers induces slight stimulation, a shift in thought processes, enhanced visual perception, and mild closed-eye visuals. Nymphaea caerulea is related to, and possesses similar activity as Nelumbo nucifera, the Sacred Lotus. Both Nymphaea caerulea and Nelumbo nucifera contain the alkaloids nuciferine and apomorphine, which have been recently isolated by independent labs.[citation needed] These psychoactive effects make Nymphaea caerulea a likely candidate (among several) for the lotus plant eaten by the mythical Lotophagi in Homer's Odyssey. Used in aromatherapy, Nymphaea caerulea is purported to have a "divine" essence, bringing euphoria, heightened awareness and tranquility.[citation needed] Other sources cite anti-spasmodic and sedative, purifying and calming properties. |
 |  Leonotis leonurus Leonotis leonurus | Both leaves and flowers (where most concentrated) contain Leonurine. (Effects reminiscent of marijuana) |
 |  Leonotis nepetifolia Leonotis nepetifolia | Both leaves and flowers (where most concentrated) contain Leonurine. (Effects reminiscent of marijuana) |
 |  Calea zacatechichi Calea zacatechichi | Produces vivid dreams after smoking. It is also employed by the Chontal people as a medicinal herb against gastrointestinal disorders, and is used as an appetizer, cathartic anti-dysentery remedy, and as a fever-reducing agent. Its psychedelic properties do not become apparent until the user is asleep. |
 |  Silene capensis Silene capensis | Produces vivid dreams after smoking. |
 | |
| Seeds contain D-lysergic acid amide, lysergol, and turbicoryn; lysergic acid alkaloids up to 0.03%[100] | |
- Catharanthus roseus is (perhaps unpleasantly) "hallucinogenic."[101]
- Vinca minor
- Ilex guayusa, which is used as an additive to some versions of Ayahuasca. According to the Ecuadorian indigenous, it is also slightly hallucinogenic on its own, when drunk in high enough quantities.
Loganaceae family:
- Desfontainia spinosa, causes visions[102]
- Heimia myrtifolia, auditory[103]
- Heimia salicifolia, auditory



No comments:
Post a Comment